参考文章:
这里打开参考文章
1. 介绍
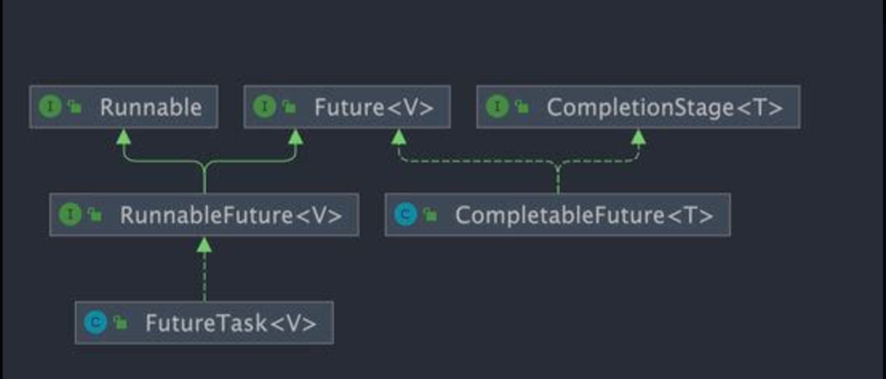
1.1 future介绍
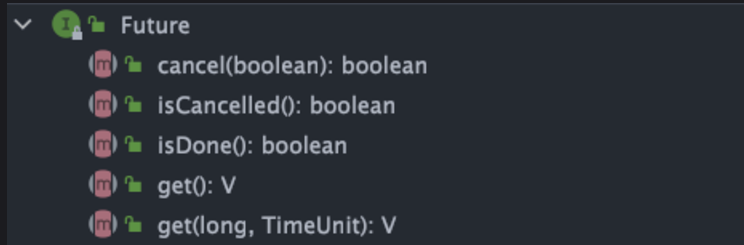
Future 类只是一个泛型接口,核心思想是异步调用,主要有5个核心API
泛型接口:编译时期有效,为了保持数据类型的一致
// V 代表了Future执行的任务返回值的类型
public interface Future<V> {
// 取消任务执行
// 成功取消返回 true,否则返回 false
boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning);
// 判断任务是否被取消
boolean isCancelled();
// 判断任务是否已经执行完成
boolean isDone();
// 获取任务执行结果
V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException;
// 指定时间内没有返回计算结果就抛出 TimeOutException 异常
V get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutExceptio
}1.2 CompletableFuture 介绍
CompletableFuture 类可以解决Future 函数式编程、异步任务编排组合 的这些缺陷
public class CompletableFuture<T> implements Future<T>, CompletionStage<T> {
}
2. api
2.1 CompletableFuture的创建
new CompletableFuture()本身不会启动任何异步任务,也不会指定线程池。它只是创建一个容器,可以后续使用runAsync()或supplyAsync()来指定任务的执行。
runAsync()和supplyAsync()默认会使用ForkJoinPool.commonPool()执行任务,但你也可以通过传入自定义的Executor来指定线程池。
主要是前两种:
-
new()
-
基于
CompletableFuture自带的静态工厂方法:
runAsync(): 不关心返回值
supplyAsync(): 接收返回值, 类型是U
static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier);
// 使用自定义线程池(推荐)
static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier, Executor executor);
static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable);
// 使用自定义线程池(推荐)
static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable, Executor executor);- 如果已经知道计算的结果的话,可以使用静态方法
completedFuture()来创建CompletableFuture
CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.completedFuture("hello!");
assertEquals("hello!", future.get());2.2 异步结果的中间处理
主要有四种:
thenApply()接收Function
CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.completedFuture("hello!")
.thenApply(s -> s + "world!");
assertEquals("hello!world!", future.get());
// 这次调用将被忽略 因为get(只接收一次异步调用结果)
future.thenApply(s -> s + "nice!");
assertEquals("hello!world!", future.get());-
thenAccept()接收Consumer -
thenRun()接收Runnable
CompletableFuture.completedFuture("hello!")
.thenApply(s -> s + "world!").thenApply(s -> s + "nice!").thenAccept(System.out::println);//hello!world!nice!
CompletableFuture.completedFuture("hello!")
.thenApply(s -> s + "world!").thenApply(s -> s + "nice!").thenRun(() -> System.out.println("hello!"));//hello! runnable接口不接收对象 所以前面的返回值传不过来whenComplete()接收BiConsumer: 两个参数, 无返回
whenComplete() 的回调方法本身是可以抛出异常的,但是如果回调函数抛出异常,这个异常不会影响原始的 CompletableFuture,它不会传播到链式调用中。也就是说,whenComplete() 抛出的异常并不会终止后续任务的执行。
CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "hello!")
.whenComplete((res, ex) -> {
// res 代表返回的结果
// ex 的类型为 Throwable ,代表抛出的异常
System.out.println(res);
// 这里没有抛出异常所有为 null
assertNull(ex);
});
assertEquals("hello!", future.get());2.3 异常处理
handle()
接收一个结果和异常, 如果异常不为空, 返回一个期望的值
CompletableFuture<String> future
= CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
if (true) {
throw new RuntimeException("Computation error!");
}
return "hello!";
}).handle((res, ex) -> {
// res 代表返回的结果
// ex 的类型为 Throwable ,代表抛出的异常
return res != null ? res : "world!";
});
assertEquals("world!", future.get());exceptionally()
接受一个异常返回一个期望值
CompletableFuture<String> future
= CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
if (true) {
throw new RuntimeException("Computation error!");
}
return "hello!";
}).exceptionally(ex -> {
System.out.println(ex.toString());// CompletionException
return "world!";
});
assertEquals("world!", future.get());
3. 多个任务的并行和串行
3.1 串行
thenCompose()
源码:
注意: ? extends CompletionStage 是返回值, 而thenApply是? extends U, 只有thenCompose返回CompletionStage
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenCompose(
Function<? super T, ? extends CompletionStage<U>> fn) {
return uniComposeStage(null, fn);
}
// 对比thenApply
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApply(
Function<? super T,? extends U> fn) {
return uniApplyStage(null, fn);
}示例:
CompletableFuture<String> future
= CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "hello!")
.thenCompose(s -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> s + "world!"));
assertEquals("hello!world!", future.get());3.2 并行
henCombine()
源码:
public <U,V> CompletableFuture<V> thenCombine(
CompletionStage<? extends U> other,
BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn) {
return biApplyStage(null, other, fn);
}示例:
CompletableFuture<String> completableFuture
= CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "hello!")
.thenCombine(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(
() -> "world!"), (s1, s2) -> s1 + s2)
.thenCompose(s -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> s + "nice!"));
assertEquals("hello!world!nice!", completableFuture.get());3.3 其他
acceptEither()
CompletableFuture<String> task = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("任务1开始执行,当前时间:" + System.currentTimeMillis());
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("任务1执行完毕,当前时间:" + System.currentTimeMillis());
return "task1";
});
CompletableFuture<String> task2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("任务2开始执行,当前时间:" + System.currentTimeMillis());
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("任务2执行完毕,当前时间:" + System.currentTimeMillis());
return "task2";
});
task.acceptEitherAsync(task2, (res) -> {
System.out.println("任务3开始执行,当前时间:" + System.currentTimeMillis());
System.out.println("上一个任务的结果为:" + res);
});
// 增加一些延迟时间,确保异步任务有足够的时间完成
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}allOf()
方法会等到所有的 CompletableFuture 都运行完成之后再返回, 类似于对所有异步任务做了个聚合
CompletableFuture<Void> task1 =
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
//自定义业务操作
});
......
CompletableFuture<Void> task6 =
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
//自定义业务操作
});
......
CompletableFuture<Void> headerFuture=CompletableFuture.allOf(task1,.....,task6);
try {
headerFuture.join();
} catch (Exception ex) {
......
}
System.out.println("all done. ");anyof()
CompletableFuture<Object> f = CompletableFuture.anyOf(future1, future2);
System.out.println(f.get());
4. 使用建议
4.1 自定义线程池
为什么: 默认会使用 ForkJoinPool 的公共线程池(ForkJoinPool.commonPool) 所有未指定线程池的 CompletableFuture 实例都会使用这个线程池。如果应用中有多个并发框架它们会共享公共线程池,可能导致任务延迟或竞争
private ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(10, 10,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>());
CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
//...
}, executor);4.2 避免使用get()
get会阻塞当前线程, 如果要使用的话需要添加超时时间
使用whenComplete提前把要执行的逻辑放到whenComplete中
4.3 正确处理异常
使用whenComplete ,handle ,exceptionally, CompletableFuture.allOf都可以处理异常
when只观察异常
handle处理异常然后返回正常值
exceptionally只有异常时处理
4.4 合理组合多个异步任务
正确使用 thenCompose() 、 thenCombine() 、acceptEither()、allOf()、anyOf()等方法来组合多个异步任务,以满足实际业务的需求,提高程序执行效率。